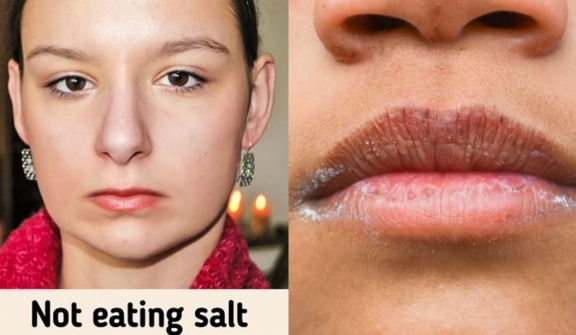

Weight gain: Iodized salt is important for hormones. When you quit salt completely, you run the risk of weight gain, facial puffiness, dry skin, muscle weakness, and fatigue.
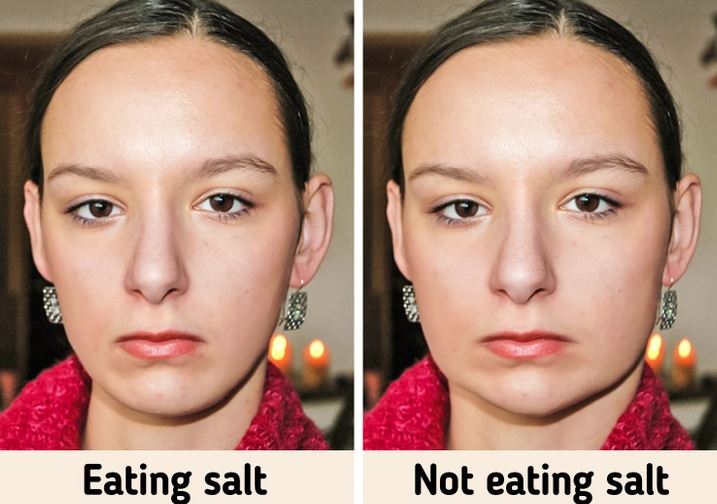

A sodium-rich diet has been shown to have many benefits for the body, especially for those with heart disease. Conversely, if you stopped eating salt, your heart disease would get worse.
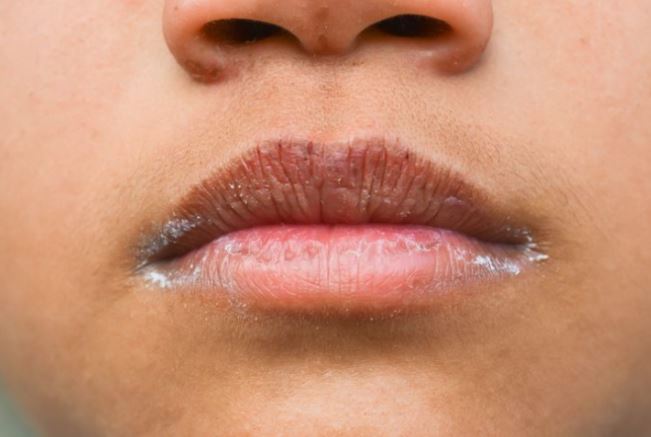
Symptoms resembling dehydration could manifest if your blood's sodium levels significantly decrease. You might encounter dry mouth, dizziness, increased thirst, and reduced frequency of urination.
Research shows that insulin resistance increases when there is not enough sodium in the body. This condition causes you to no longer respond well to insulin, causing your blood sugar to be higher than normal.
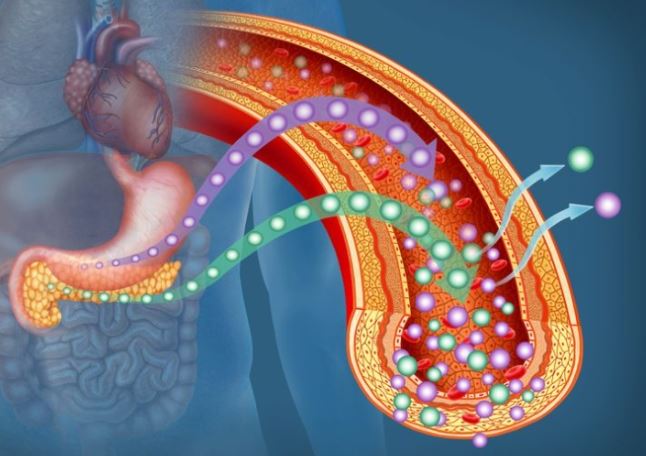

While the condition doesn't often exhibit early symptoms, scientists note that reduced salt intake can lead to more noticeable symptoms such as nausea and vomiting when cholesterol levels are affected.




