
In a recent scientific breakthrough, microscopic creatures that had been frozen for 46,000 years in the Siberian permafrost were revived.
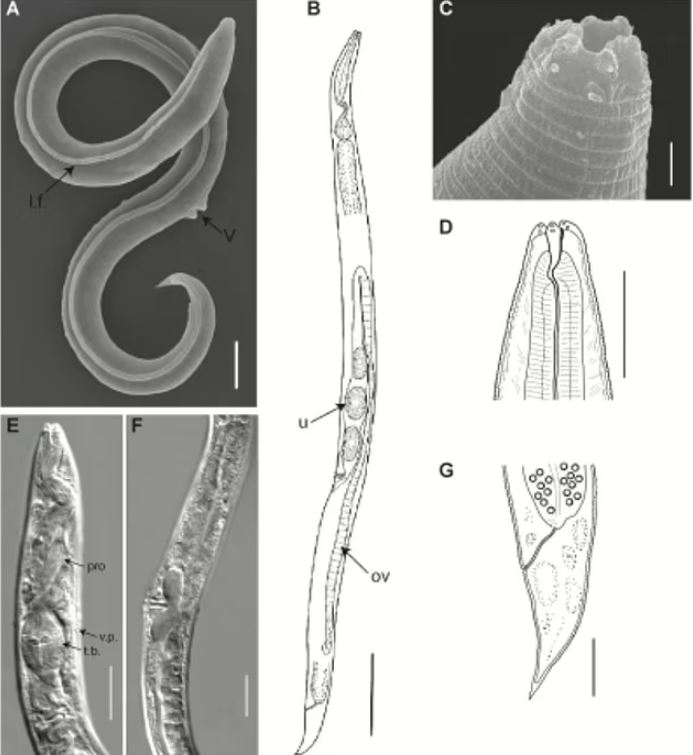
These ancient roundworms, also known as nematodes, have the remarkable ability to enter a state of anabiosis, where their bodies able to shut their bodies down in unsuitable environments
After being discovered in a frozen squirrel burrow in 2018, scientists simply put the worms in water to wake them from their dormant state.
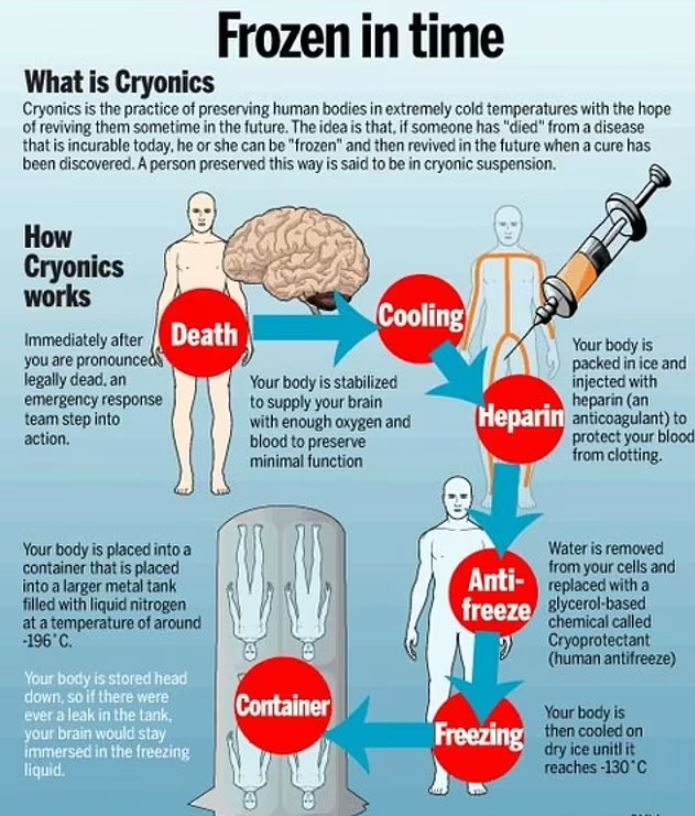
When asked about the potential revival of human-frozen could be resurrected by similar means, a cryonics expert admitted the differences in cryopreservation of humans and animals. However, they said that technological advancements could make it possible for individuals to make a remarkable comeback, much like the fictional character "Encino Man," in the next 50-70 years.
In a recent interview with MailOnline, Valeriya Udalova, the CEO of KrioRus, a Russian cryogenics company that houses 94 frozen corpses in its facilities in the capital city, said: “I don’t think that human metabolism can be radically restructured so that we also go into anabiosis like animals. It’s probably easier to create new, artificial bodies."
Valeriya Udalova said that worms are not the only organisms capable of undergoing anabiosis, as the process also extends to frogs and Siberian anglerfish. However, Udalova pointed out that humans do not possess the same abilities.
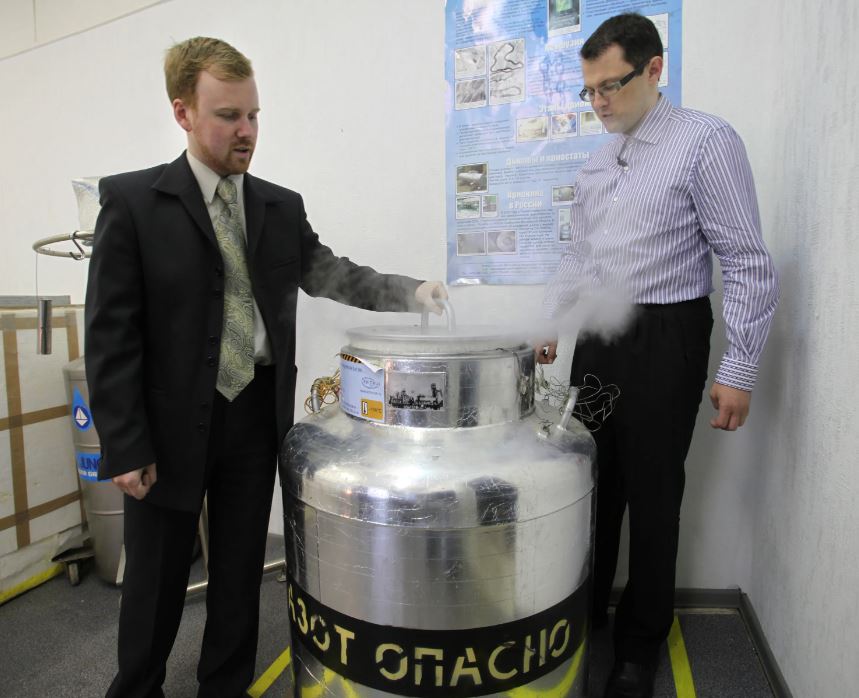
At KrioRus, surgeons perform a procedure that involves draining the blood from human bodies before connecting them to a new circulatory machine filled with cryoprotectant solutions, which protect cells and tissues.
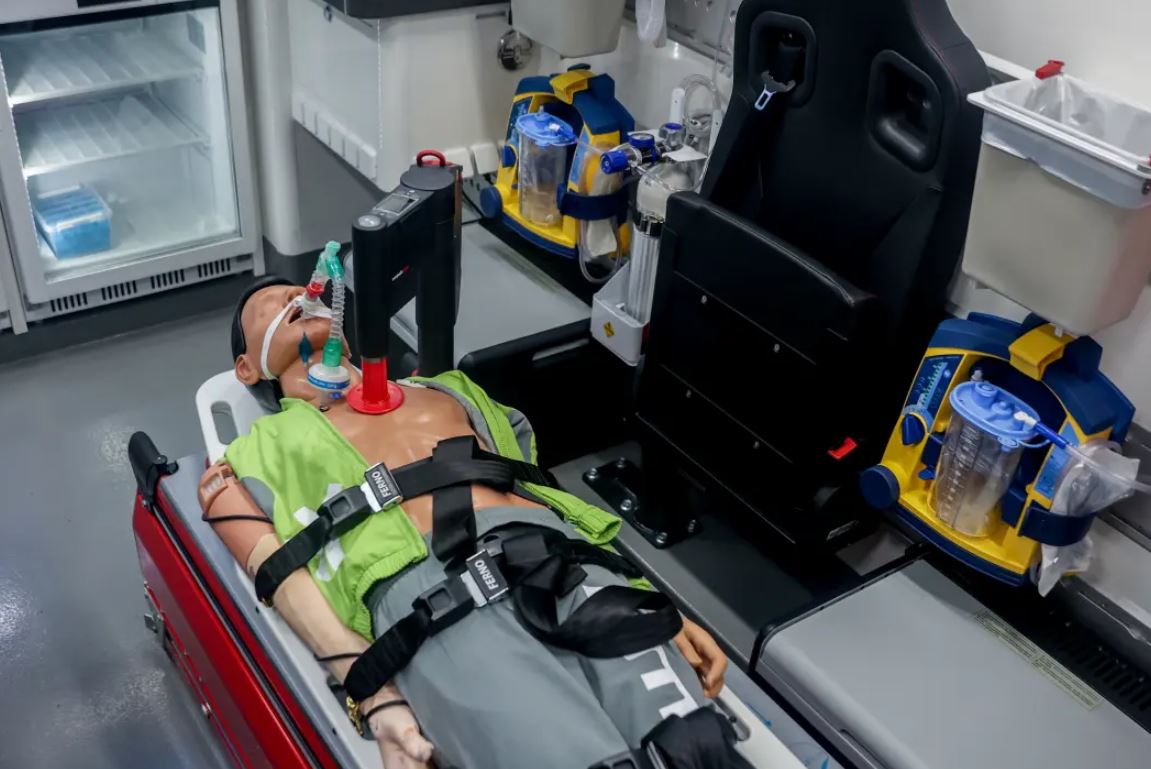

It is crucial for the deep-freezing process to begin within minutes of someone being declared legally dead. The bodies are then frozen at a temperature of -321°F.
Typically, the preservation of bodies involves the use of anti-freeze chemicals, such as ethylene glycol, which are commonly used to protect intact cells and tissues in other areas of scientific research.
The bodies are gradually cooled to reach an extreme temperature of -196°C (-321°F) and are then held in chambers until new technology arises. However, this process is far from simple, as the chemicals utilized for preservation purposes can have toxic effects with prolonged exposure.

Additionally, the gradual cooling of frozen organs can potentially lead to life-threatening fractures if the rates of melting are not consistent throughout the body.
So, significant progress in tissue engineering and medicine would be necessary to revive frozen bodies.
According to Udalova, there would have to be major strides in medicine for humans to be able to be resurrected. This possibility may occur within the next 50-70 years.

Dr. João Pedro de Magalhães, a Portuguese microbiologist, asserts that current technology falls short because the cryoprotectant agents used have "toxic" effects on the brain and other body parts




