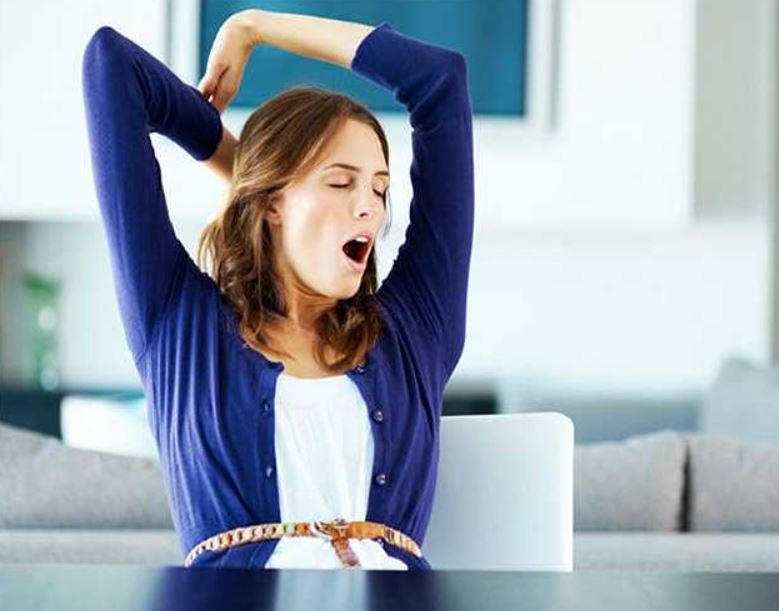


When people wake up, it is common for them to involuntarily stretch and yawn. These two behaviors are considered instinctive in humans, as well as in animals. However, both behaviors offer numerous health benefits.
During sleep, our muscles relax and fluid accumulates along our back due to gravity. Upon waking up, stretching helps in massaging the fluid, assisting its gradual return to its normal position.
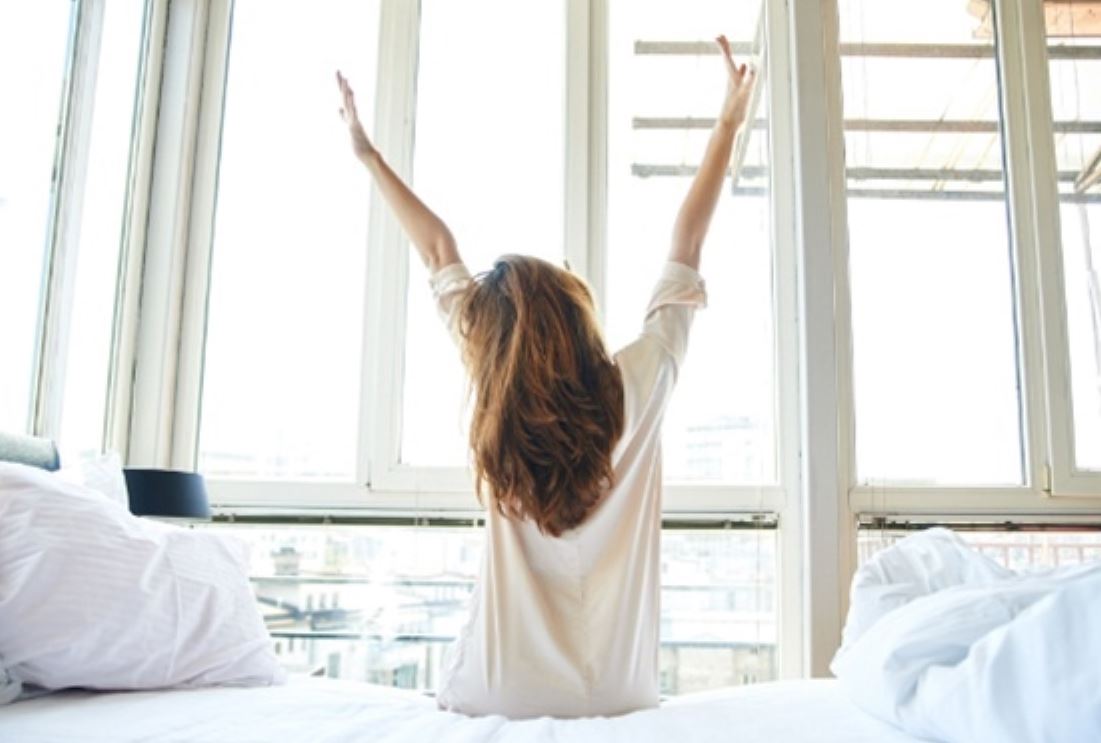

The moment you wake up, you instinctively stretch your muscles, causing the bodily fluids to return to their normal positions. This stretch also helps release resting muscles to work again.
When we wake up, yawning and stretching at the same time help improve blood flow, which automatically reduces stress.

This occurs as the nervous system, which regulates functions such as heart rate, digestion, and hormone secretion, receives a boost.
When we stretch after waking up, our joints and muscles start working again. This action signals the brain that it is time to wake up.
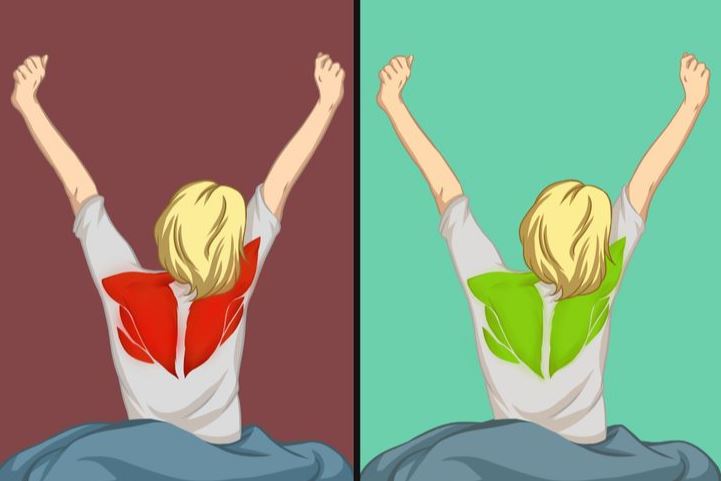

When we stretch and yawn, we promote the re-establishment of communication between the brain and muscles, resulting in stronger signals from the brain to the muscles.
The subsequent feedback received back lets the brain work to calibrate the strength of these signals for performing different tasks.
Finally, yawning and stretching are comforting actions that help us stay awake.




