NASA has recently made a groundbreaking discovery, locating a "super-Earth" planet that could potentially meet the needs of human life in outer space.
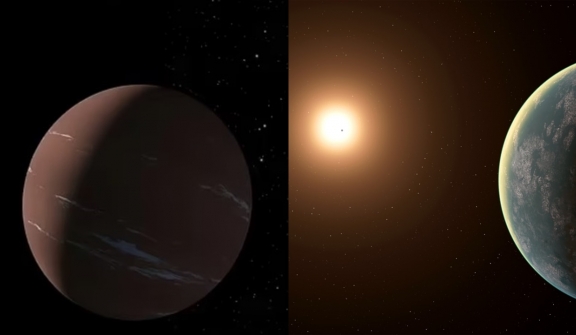
This remarkable finding reveals that the planet named TOI-715 b is situated 137 light-years away from Earth.
TOI-715 b, with a size 1.5 times larger than Earth, orbits a small, reddish star within the habitable zone.
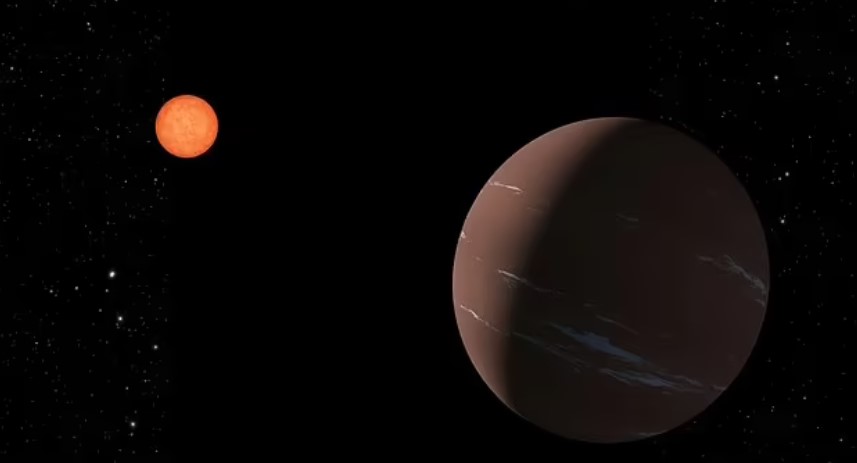

This zone refers to the region around a star where conditions are suitable for liquid water to exist on a planet's surface, a crucial factor for supporting life as we know it.
The exoplanet was discovered using the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which was launched by NASA six years ago to observe planets outside our solar system.
The satellite detected clues of TOI-715's existence, leading an international team of scientists, led by the University of Birmingham, to further investigate its properties.
An interesting characteristic of TOI-715 b is its tight orbit, completing one revolution every 19 days.
This rapid orbit means that one side of the planet constantly faces its star, resulting in extreme temperature variations between the day and night sides.
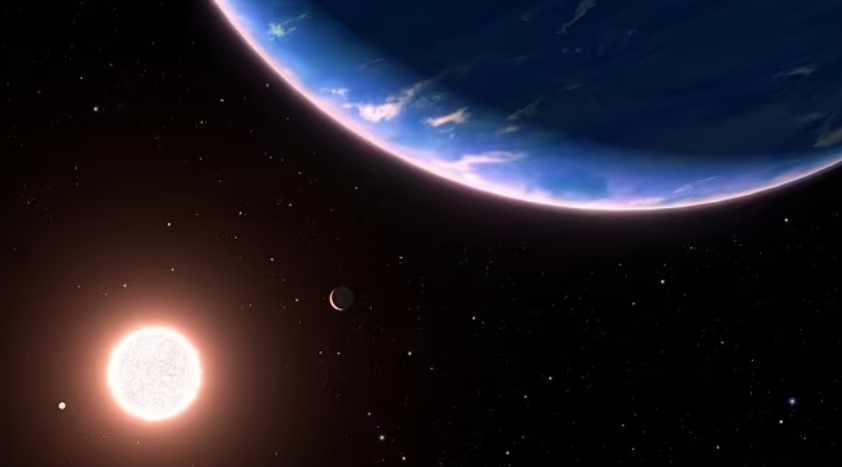

These temperature differentials could significantly impact climate and weather patterns on the planet.
The research team believes that this system may also contain a second Earth-sized planet.
Confirming the existence of this potential companion planet would make it the smallest habitable zone planet discovered by TESS to date.
The discovery of a second planet within this system would provide further opportunities to study and analyze its atmosphere, potentially searching for signs of life.
Although super-Earths are not uncommon in the universe, with NASA having discovered over 5,000 exoplanets to date, TOI-715 b stands out due to its potential habitability.

Not all super-Earths are suitable for life, as some may have extreme temperatures or be entirely covered in water. However, this newly discovered planet holds promise for supporting life, given its size and location within the habitable zone.
The ongoing exploration of exoplanets continues to fuel excitement and curiosity among astronomers and space enthusiasts.

Through advancements in technology and the use of powerful telescopes like NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), scientists hope to gain further insights into these distant worlds and potentially unravel the mysteries of alien life.




