
A recent study conducted by researchers has revealed a surprising connection between wearing jeans and environmental impact.
The findings suggest that the carbon footprint of fast fashion jeans can be as harmful to the environment as driving a car.

The recent revelation that wearing jeans can be as harmful to the environment as driving a car has left people feeling confused and concerned.
A study conducted by researchers from the Guangdong University of Technology in China shed light on the carbon footprint of fast fashion consumption, with a particular focus on the production and lifecycle of jeans.
The study, led by Ya Zhou, uncovered that jeans have a significant impact on the environment, a fact that may surprise many.

It raises an important question for those who frequently wear jeans: Do they opt for fast fashion brands that offer lower quality and shorter lifespan, or do they choose more environmentally friendly brands that provide higher quality and durability?
The environmental consequences of the fast fashion industry are vast and include water use, chemical pollution, CO2 emissions, and textile waste.
To determine the extent of damage caused by a pair of fast-fashion jeans, the researchers utilized the lifecycle assessment method.
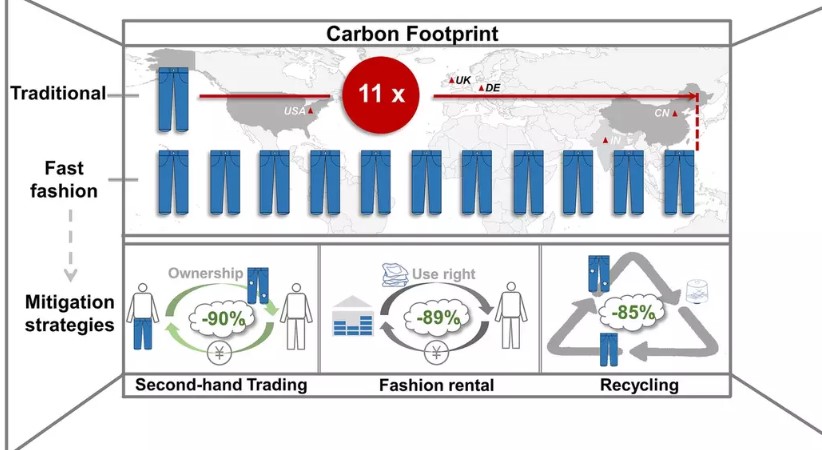
They tracked the journey of jeans from their raw cotton form to their disposal in an incinerator.
The results were surprising.
The carbon footprint of fast fashion jeans is about 95-99 percent higher than that of ethically responsible jeans.
In reality, wearing a pair of fast-fashion jeans contributes approximately 2.50 kg of carbon dioxide (CO2e), which is 11 times higher than the carbon footprint of traditional fashion consumption.
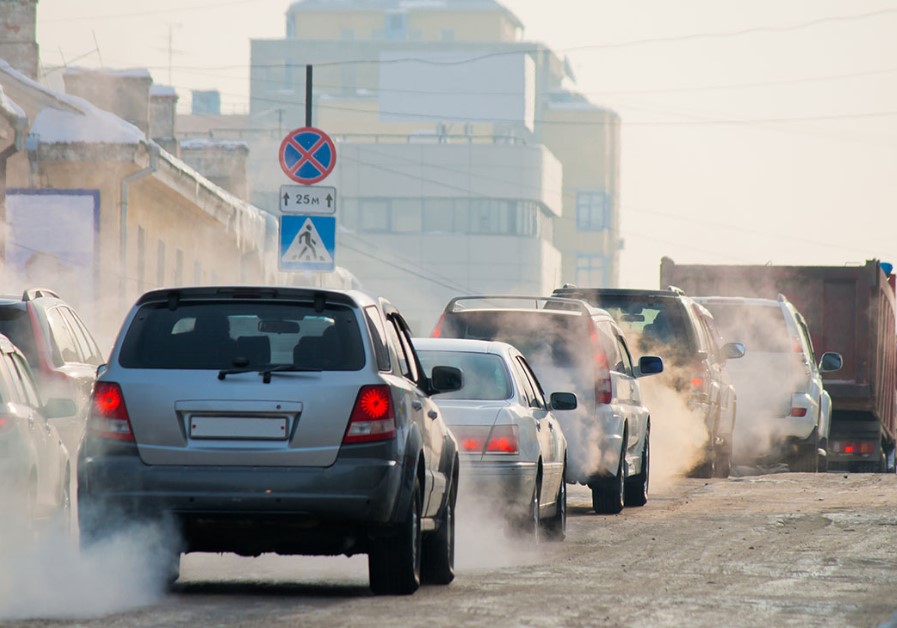

To put it simply, wearing jeans is equivalent to driving a regular gas-powered car for approximately 6.4 miles in terms of carbon emissions.
The research also highlighted that the production of fiber and jeans is the major contributor to the carbon footprint of fast fashion, accounting for 70 percent of the total impact.
Additionally, it revealed that fast-fashion jeans are typically worn only around seven times, whereas slow-fashion jeans are worn approximately 120 times on average.

People want to stay fashionable and constantly buy new clothes, but they don't keep them for long.
This behavior uses up more resources and energy at every stage of the clothing production process. Finally, this excessive consumption worsens the clothing industry's contribution to climate change.




