
Electric cars have long been hailed as the future of transportation, and their impact on energy consumption has become a topic of interest.
Recently, a Tesla driver shared their first electric bill, revealing a surprising revelation that has left people astounded and sparked discussions about the potential of electric vehicles in reducing energy costs.
In a surprising turn of events, the electric bill of a Tesla owner for an entire year turned out to be astonishingly low, totaling just $2.37.
This unexpected revelation challenges the belief that electric vehicles come with exorbitant expenses.
After taking a closer look, it was discovered that the Tesla driver had a special device called a Tesla Powerwall installed.
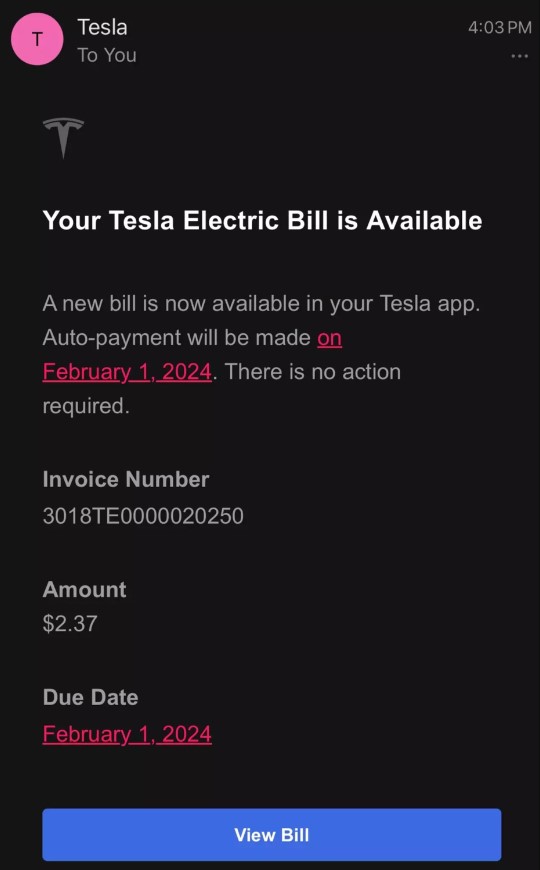
This Powerwall was connected to solar panels, which not only generated electricity for the house but also stored extra energy to charge the Tesla car.
The Powerwall is an advanced solar battery system designed to store energy from home solar panels or roofs.
It features a lithium-ion battery with a capacity of 13.5kWh and a 100% depth of discharge, ensuring optimal utilization of stored energy. The Powerwall is not only a backup during power outages but also enables users to potentially go off the grid.
Purchasing a single Powerwall comes with a price tag of $11,500, with costs varying based on location.

However, there are discounts available for those considering multiple units, making it an attractive option for those seeking a comprehensive home energy solution.
The overall costs, including installation and pricing for different quantities, can be broken down for interested buyers.
The number of Powerwall units needed depends on the intended usage. For full-house backup power, experts suggest three to four Powerwalls, while one to two units may suffice for partial coverage.
Tesla offers two models to choose from: the standard Powerwall 2 and the Powerwall+ with an integrated solar converter.

Both models have a capacity of 13.5kWh, but the Powerwall+ stands out with double the backup power output and more on-grid power.
The choice between the two depends on individual energy requirements and preferences for an all-in-one solution.
The Powerwall functions as a lithium-ion battery, storing solar energy for future use and seamlessly integrating with the home's electrical system.
The inverter converts stored DC electricity into AC, ensuring compatibility with household power supplies.

Tesla places great emphasis on the durability of its Powerwall, taking measures like regular software updates to prevent battery wear and tear.
The Powerwall incorporates advanced features like lithium-ion cells, thermal management, and smart charging algorithms, all of which work together to enhance its efficiency.
While there are advantages such as improved solar efficiency and installation flexibility, there are also considerations to be made.

The upfront cost of the Powerwall is significant, and the capacity differences and potential need for multiple units should be weighed against individual energy needs and budgets.
Additionally, installation wait times should be considered, although federal tax credits are available for those who invest in Tesla Solar and Powerwall before 2032.




